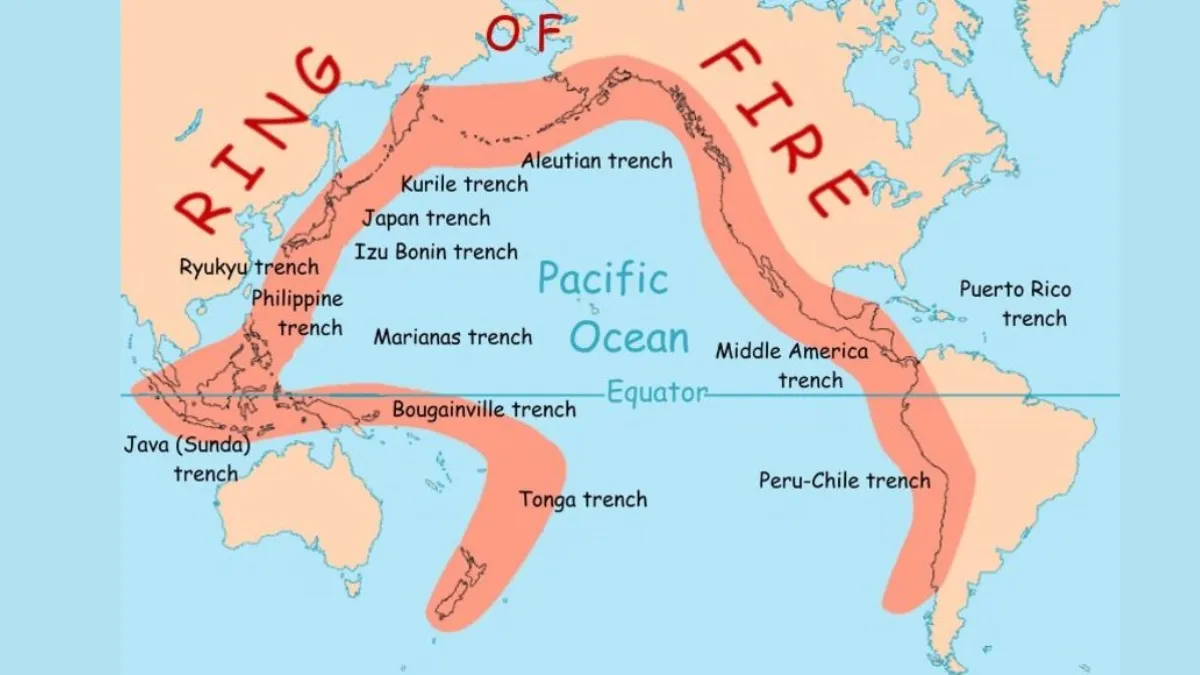
What is the Pacific Ring of Fire?
The Ring of Fire, which is commonly known as the Circum-Pacific Belt, is a path along which many active volcanoes and frequent earthquakes characterise the Pacific Ocean. It is largely composed of results of Plate Tectonics, where massive plates of the Pacific interact with less dense plates surrounding them.
Why is the Pacific region called the Ring of Fire?
The Pacific region is called the Ring of Fire because it is a horseshoe-shaped zone around the edge of the Pacific Ocean that is prone to earthquakes and has numerous active volcanic areas. These areas experience intense tectonic activity, making it one of the most geologically dynamic regions of the Earth.
What are the reasons for the Pacific region being given the name “Ring of Fire”?
Reasons for which the Pacific region is being given the name “Ring of Fire” is:
1. Tectonic Plate Boundaries:
The Pacific Plate is surrounded by several tectonic plates, like South America, Eurasia, the Philippines and Indo-Australia. The consistent movement and collision of these plates lead to a subduction zone where one plate is forced under, which triggers the earthquake and volcanoes.
2. Volcanic Activity:
About 75% of the world’s active volcanoes are located in the Ring of Fire. Countries like the Philippines, Chile and the US experience frequent volcanic eruptions.
3. Earthquake Frequency:
Around 90% of the world’s earthquakes occur in this region. Major fault lines, such as the San Andreas Fault in California and the Japan Trench, are part of this region only.
Geographical stretch of Ring Of Fire
The Pacific Ring of Fire is stretched approximately 40,000 km, tracing the boundaries between several tectonic plates. This region covers South and North America, from the western coast, which crosses over the Aleutian Islands of Alaska and runs down to the eastern coast of New Zealand and the northern coast of Alaska.
How many countries are included in the Ring of Fire?
There are 8 countries which are included in the Pacific Ring of Fire, which are:
-
Japan
-
Indonesia
-
Philippines
-
New Zealand
-
Chile
-
Peru
-
United States (West Coast)
-
Russia (Kamchatka Peninsula)
Conclusion
The term “Ring of Fire” reflects the circular pattern of volcanoes and earthquake zones that ring the Pacific Ocean, which is created by active plate tectonics. It is one of the most geologically hazardous areas in the world.