Show Key Points
The human brain is an impressive example of biological engineering, and at the top is its largest part: the cerebrum.
Making up about 85% of the brain's weight. It controls everything that makes you unique, from your memories to your ability to recognise faces.
But do you know that, though it is the largest part of the brain, its size doesn't make it unique? This part of the brain is responsible for shaping your personality. Even a small change in one part can affect your entire experience.
In this article, we'll take a look at the functions of the cerebrum and explore the specific lobes of the cerebrum and what they do.
ALSO READ| Which Is The Longest And Smallest Bone In The Human Body?
Which is the Largest Part of the Brain?
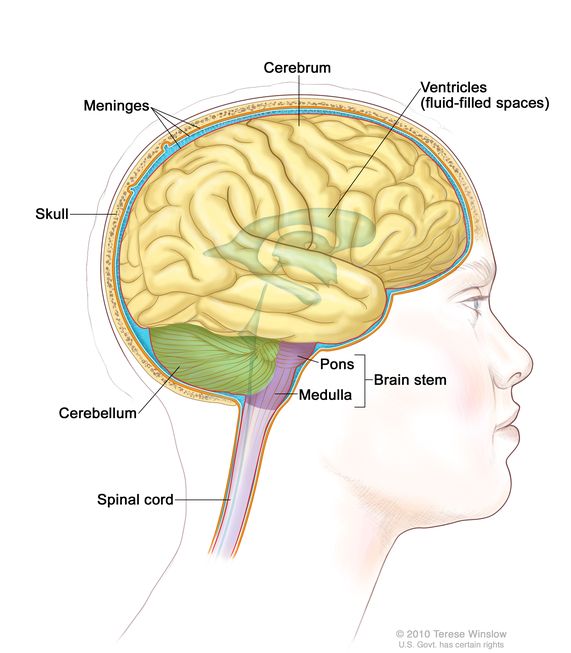
Source: NCI
The cerebrum is the largest part of the brain, making up about 85% of its total weight. It sits at the top of the skull, above the cerebellum and brainstem. This is the part of the brain responsible for thinking, which helps set humans apart from most other species.
> Functions of the Cerebrum
As the primary "command centre", the cerebrum handles the most advanced functions of the human body. Its responsibilities are vast:
- Sensory Processing: It interprets signals from your eyes, ears, nose, and skin.
- Motor Control: It initiates and manages all voluntary muscle movements, like walking or typing.
- Higher Intelligence: This is where problem-solving, logic, learning, and creativity happen.
- Emotions and Speech: It allows you to feel complex emotions and form words to express them.
- Memory: It stores both short-term and long-term memories.
What Does a Cerebrum Look Like? [THE STRUCTURE OF CEREBRUM]
The cerebrum looks like a large, wrinkled, greyish-pink walnut. Its surface is not smooth; it is covered in deep folds and ridges.
- Gyri: These are the elevated ridges or "bumps" on the surface.
- Sulci: These are the small grooves or furrows between the bumps.
- Fissures: These are the very deep grooves that divide the brain into major sections.
This folded structure is a brilliant example of nature's design. By wrinkling the surface, the brain can pack more grey matter (neurones) into the limited space of the human skull. If you unfolded the cerebrum, it would cover an area roughly the size of a large pillowcase.
MUST READ| List of Organs in a Human Body
What are the Different Parts of the Cerebrum?
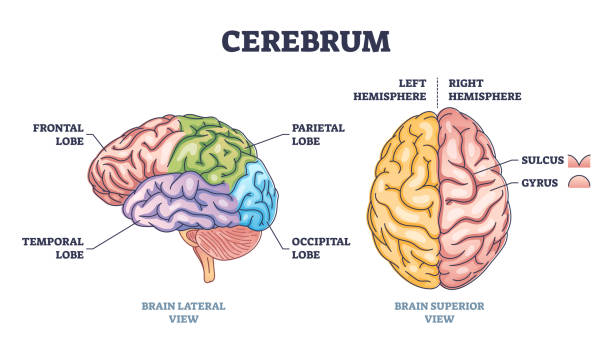
Source: iStock
The cerebrum is divided into two main halves, called hemispheres, which are connected by a bundle of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum.
> Left vs. Right Hemisphere
You might have heard a friend say that you are either left-brained or right-brained. The question of "Left Brain" versus "Right Brain" has long interested neuroscientists.
As mentioned above, these two ‘sides’ of the brain are always in contact through the corpus callosum, but each side usually handles different kinds of tasks. This means that the cerebrum works as a unified whole.
For example, while the left side processes the literal meaning of words, the right side helps you understand if someone is being sarcastic. You need both to hold a simple conversation.
Here’s how the two sides of the brain usually share different types of work:
| Feature | Left Hemisphere (The "Analyst") | Right Hemisphere (The "Artist") |
| Primary Focus | Logic, facts, and sequencing. | Imagination, feelings, and rhythm. |
| Language | Spoken words, grammar, and writing. | Tone of voice, context, and non-verbal cues. |
| Math & Science | Numerical skills and complex calculations. | Spatial ability and patterns. |
| Perspective | Focuses on fine details (the "trees"). | Focuses on the big picture (the "forest"). |
| Motor Control | Controls the right side of the body. | Controls the left side of the body. |
> Lobes of the Cerebrum
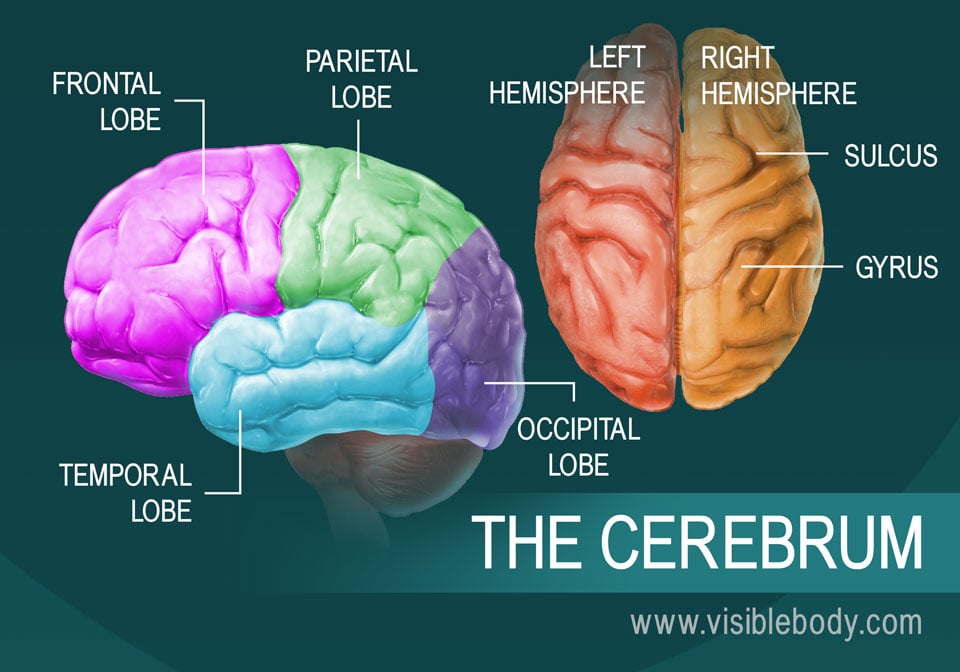
Source: Visible Body
Additionally, each hemisphere is further divided into four distinct lobes:
| Lobe | Location | Primary Role |
| Frontal Lobe | Front (forehead) | Reasoning, planning, and voluntary movement. |
| Parietal Lobe | Top Middle | Processing touch, pressure, and spatial orientation. |
| Temporal Lobe | Sides (near ears) | Hearing, memory, and language comprehension. |
| Occipital Lobe | Back | Visual processing and interpreting what we see. |
Conclusion
The human brain is an amazing organ, and the cerebrum is its most important part. As the largest section, it does much more than take up space. It lets you think, speak, and remember everything around you.
- The Largest Part: The cerebrum makes up 85% of your brain's weight.
- Unique Structure: Its folded surface (gyri and sulci) creates more space for brain power.
- Four Major Lobes: Each section, Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital has a specific job.
- Two Hemispheres: The left and right sides work together to balance logic and creativity.
The cerebrum’s left side helps with logic, while the right side supports creativity. It is always working to keep you going. Its wrinkled surface holds billions of neurones that control everything you do.
WHAT'S NEXT| Which Is the Largest Organ of the Human Body?
Source: MedlinePlus (Brain Components)
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation