Key Points
- The Union Budget, mandated by Article 112, is presented annually in Parliament.
- Since 2017, the Union Budget has been presented on February 1st each year.
- The Budget includes estimates, revised estimates, and actuals for finances.
Union Budget 2026: The budget is an Annual Financial Statement which is mandated under Article 112 of the Indian Constitution and therefore, it becomes necessary for the government to present the budget in the Parliament. It is a mandatory exercise for the Union Government to present a budget annually. The Union Budget has been presented on 01st February every year since 2017. Previously, the budget used to get presented in the last week of February. The budget is being prepared by the Budget Division of the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance.
What is the Union Budget?
The Union Budget is like a balance sheet of the expected yearly expenditures and incomes of the government. The Ministry of Finance prepares the budget with a total expected outlay and allocations to each department of the government. The budget outlines what are the assets and liabilities of the government, and how the government is going to manage them. The Union Budget consists of three categories:
-
Budget Estimates (BE): Upcoming financial year projections
-
Revised Estimates (RE): Updates estimates for the current financial year
-
Provisional Actuals (PA): Actual receipts and expenditures for the previous financial year
Types of Budgets in India
In India, the Union Budget is of two types: Revenue Budget and Capital Budget. The Revenue Budget is further classified into Revenue Receipts and Revenue Expenditure. The Capital Budget consists of two components: Capital Expenditure and Capital Receipts.
Revenue Budget
The Revenue Budget of the government includes the income of the government and the day-to-day expenditure of the government.
-
Revenue Receipts: This includes the income by the government which is an asset and not a liability. It includes tax and non-tax revenue receipts.
-
Tax Receipts: Includes income tax, corporation tax, etc.
-
Non-Tax Receipts: Includes interests on loans and dividends.
-
Revenue Expenditure: The revenue expenditure is the expenses of the government which the government will spend and will never get any return.
Capital Budget
The capital budget demonstrates the government’s assets and liabilities that it will generate and create and the funds required for development.
-
Capital Receipts: The capital receipts all those funds that reduce the assets and create liabilities on the government. Examples:
-
Debt: These receipts create debt on the government. These can be loans and borrowings
-
Non-Debt: The non-debt creating capital receipts can be recovery of loans, disinvestment proceeds, etc.
-
Capital Expenditure: It includes those expenses of the government which generates assets for the long-term. This also includes investments by the government. Examples: Infrastructure creation, loans to States/UTs, shares in PSUs, recovery of loans, etc.
How is the Budget Prepared?
The Government Budget is prepared by the Budget Division of the Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance.
What are the Stages of the Government Budget in Parliament
The Budget is presented by the Finance Minister in the Parliament every year on 01 February. The Budget is a step-by-step process which includes the following stages:
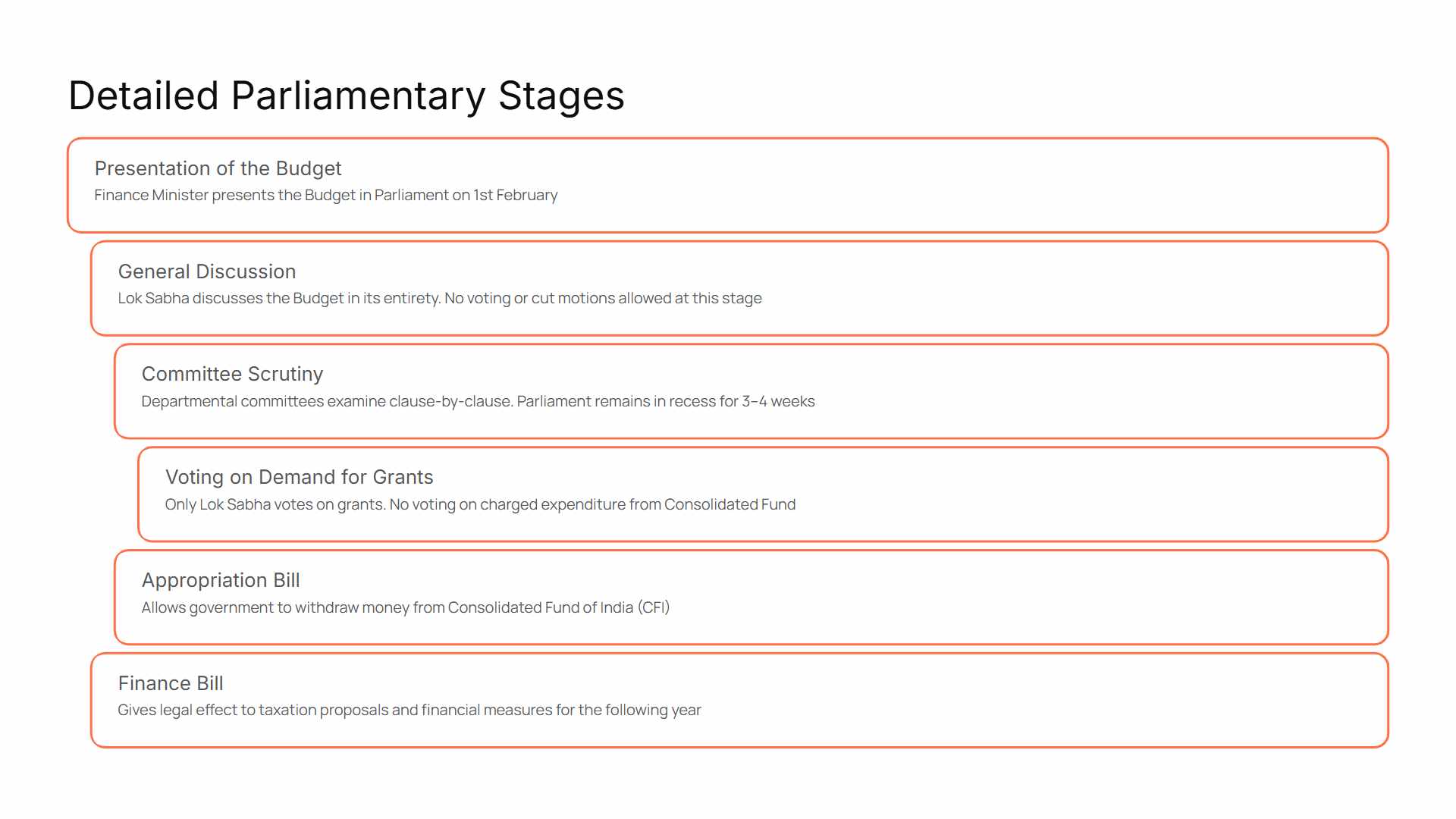
-
Presentation of the Budget: By the Finance Minister.
-
General Discussion: After the budget is presented in the Parliament, the Lok Sabha can discuss the budget in its entirety or clause by clause. In this stage, no cut motion can be passed, and no vote of accounts can be done.
-
Scrutiny by Departmental Committees: There are departmental committees which scrutinise the budget clause-by-clause. This usually takes three to four weeks and the house remains in recess for this period.
-
Voting on Demand for Grants: After the report of committees have been submitted, the budget is put to vote. Only the Lok Sabha is allowed to vote on the demand for grants. No vote is put forth for the expenditure charged on the consolidated fund of India.
-
Passing of Appropriation Bill: Government cannot withdraw the money out of the Consolidated Fund of India (CFI) with the appropriation bill. Therefore, an Appropriation Bill is introduced in the Parliament which provides for the appropriation out of the CFI.
-
Passing of Finance Bill: The Finance Bill is introduced to give effect to the financial proposals of the Government of India for the following year.
What is an Interim Budget?
The interim budget is presented when the General Elections are due in that year. The Union government at that time presented an interim budget which includes all the necessary details for the next few months until the general elections are held rather than the proposed expenditure for the whole fiscal year.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation