Carbon is found all around the Earth, including in our bodies. While most of the carbon can be found in the geosphere, it is also found in all living things, soil, in the ocean, and in the atmosphere.
It is also considered a primary building block of life, along with DNA, proteins, sugars, and fats. There are many different compounds of carbon, but among them, carbon dioxide is the most important.
At the same time, rock carbon is also a major carbon component of limestone, coal, oil, and gas.
But what is the carbon cycle, and what are the different human activities that affect the rate of exchange and distribution of carbon on the Earth?
Let’s dive into this article for more details.
What is the Carbon Cycle?
As we know, Carbon is everywhere on the Earth, but it does not stay in one place; rather, it keeps moving from one part of the Earth to another. They also transferred between the ocean, atmosphere, soil, and living things over time scales of hours to centuries.
This movement of carbon in our atmosphere through the planet, including the process of adding and removing carbon in our atmosphere, is called the Carbon Cycle.
Carbon dioxide is important because it helps keep our planet warm. It traps some of the Sun’s heat, which makes Earth comfortable for living things.
But if too much CO₂ builds up in the air, the planet becomes hotter than normal. This can affect weather, oceans, ice, and sea levels.
Also Read: Top 10 Countries with the Largest Forest Carbon Sinks (2021-2025): Check Where does India Stands
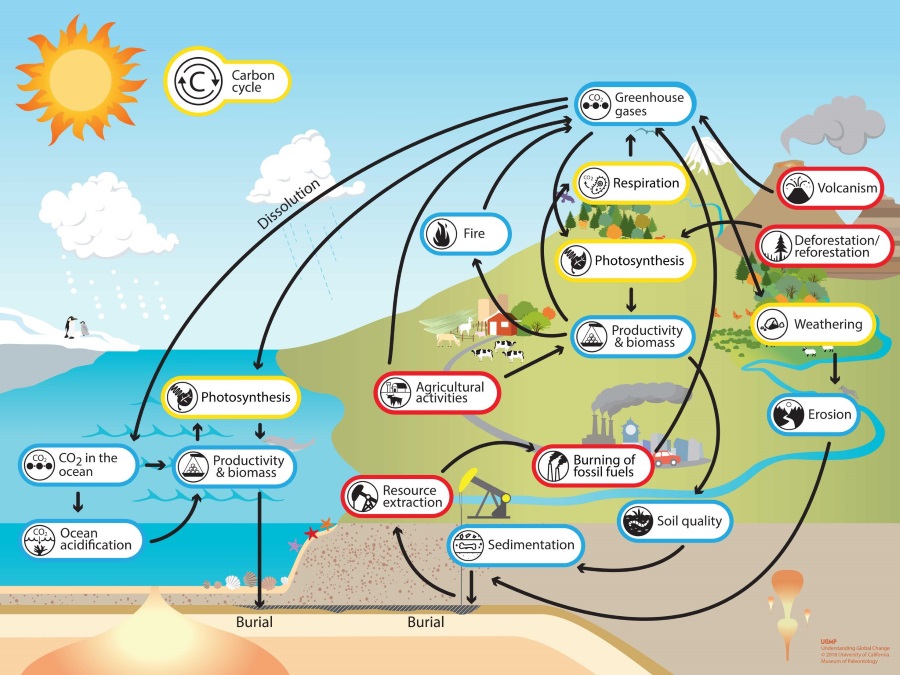
Source: University of California
How Does the Carbon Cycle Work?
Take a deep breath in. Now breathe out.
When you breathe out, you release carbon dioxide. All living things do this — humans, animals, even tiny organisms. That means we are all part of the carbon cycle.
The carbon cycle explains how carbon moves around the planet and how it enters and leaves the atmosphere.
Also Read: Why are Forests called Green Lungs of the Earth?
What is Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)?
Carbon dioxide is a gas made of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. That is why it is called CO₂. It is one of the main greenhouse gases in Earth’s atmosphere.
Why is CO₂ Important?
Greenhouse gases trap heat from the Sun. This process is called the greenhouse effect. Without it, Earth would be too cold for life.
However, if there are too many greenhouse gases, more heat gets trapped. This causes the planet to warm up, leading to:
-
Climate change
-
Rising sea levels
-
Melting snow and ice
-
Stronger or unusual weather patterns
How have human activities affected the rate of exchange and the distribution of carbon in the Earth's System?
Throughout the Earth’s history, carbon dioxide levels have naturally gone up or down, and when carbon dioxide level is increasing, the temperature of the Earth also increases.
But in the last 150 years, there have been many human activities involved that affected both the rate of exchange and the distribution of carbon in the Earth’s system, including:
| Factor / Activity | How It Affects the Carbon Cycle and Climate |
| Burning Fossil Fuels |
|
| Agriculture and Farming |
|
| Deforestation |
|
| Melting Permafrost |
|
| Burial of Organic Matter (Long-Term Changes) |
|
| Rock Cycle Processes |
|
| Volcanic Activity |
|
Source: Understanding Global Change
Conclusion
The carbon cycle is vital and plays an important role in our atmosphere, which keeps life in a balanced way on our planet.
The carbon is not static, rather then itr keep moving between air, land, oceans, and living things.
Carbon dioxide is essential for our life, in photosynthesis, and in the growth of plants, but too much of it can warm our planet.
Today, due to many different human activities, extra carbon dioxide is being added to the atmosphere, which is changing the balance of the carbon cycle.
Understanding how carbon moves around Earth, we can better protect our planet for the future.
If you have any questions, do comment, and share this article with your friends. For more such articles, visit Jagran Josh.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation