Plants are of fundamental importance for life on Earth. Plants are the main source of oxygen on which life exists. As we know, plants are the living organisms that cover a large area on Earth and provide essential resources for humans and other living things. Plants are the vital producers of food resources, give oxygen, and play a vital role in climate regulation. On Earth, there are different types of plants that are found in different shapes and in different colours, including trees, shrubs, herbs, and small grasses.
But do you ever try to find out how plants prepare their food? As a living organism, you need food to survive. So, how are plants surviving, how are they preparing food for themselves, how are they helping in nature, and how important are they for human lives? So, to know all the answers to these questions, let's dive into this article in detail.
What is Photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight for energy to produce glucose and oxygen from carbon dioxide and water.
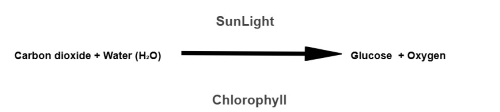
Most living things are dependent on the photosynthesis process, in which they use water from the soil and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere; these organisms produce glucose, which is a type of sugar that stores energy and releases oxygen into the atmosphere for living organisms to breathe.
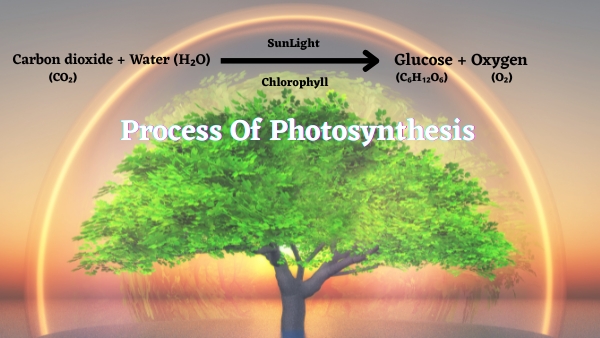
How does photosynthesis work?
Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere and water (H₂O) from the soil. Inside the plants, these two elements undergo a chemical transformation with the help of sunlight. Then these water molecules are split to release oxygen (O₂), while carbon dioxide is used to form glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆). All these processes which happen are the processes of photosynthesis in the presence of sunlight, but all these processes happen in plants due to the special structure inside the plant cells called chloroplasts.
| Point to Remember: A chloroplast is an organelle where photosynthesis processes take place in the presence of sunlight. |
What is the role of the chlorophyll?
Inside the plant's cell, each pigment of the chloroplast contains green pigment, which is called chlorophyll. These pigments are essential because they capture the sunlight. These pigments absorb blue and red wavelengths of light and reflect green. That’s why most of the leaves of plants appear green to our eyes.
How many phases are there in photosynthesis?
There are two phases in Photosynthesis, which are:
1. Light-dependent reactions: These occur in the thylakoid membrane, and they require sunlight. In this phase of photosynthesis, chlorophyll absorbs the light and helps produce energy-rich molecules – ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) & NADPH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate).
2. Light-independent reactions: In this phase of photosynthesis, this reaction takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast, and it does not require sunlight directly. Instead of using direct sunlight, they use the stored energy from ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose.
| Points to be Remembered: The stroma of the chloroplast is the fluid-filled space inside the inner membrane of the chloroplast, surrounding the grana (stacks of thylakoids) |
How many types of photosynthesis are there?
There are two primary types of photosynthesis, which are
1. C3 Photosynthesis: This type of photosynthesis is used by most plants. It creates a three-carbon molecule as the first step of photosynthesis in the Calvin cycle. These types of photosynthesis work best in cooler and wetter conditions.
2. C4 Photosynthesis: This type of photosynthesis is used in hot and dry areas. It starts with creating four-carbon molecules that help the plants to capture the carbon dioxide more efficiently, allowing them to survive in tough environments with less water and light.
Importance of Plants
| Category | How Plants Serve Us and Nature |
| Shelter & Ecosystems | Plants create homes and havens for a myriad of other living organisms, forming the very foundation of diverse ecosystems. |
| Medicine & Health | Many of the crucial compounds and ingredients used in our medicines, offering healing and relief, are derived directly from plants. |
| Resources & Materials | From the homes we build to the tools we use, plants provide essential building blocks and materials that have shaped human civilisation. |
| Energy & Fuel | Throughout history and even today, plants have been a fundamental source of fuel, powering our lives and industries in various forms. |
| Soil Health | As they complete their life cycle, plants enrich the soil through decomposition, naturally fertilising it and fostering a fertile ground for future growth. They also act as natural binders, preventing soil erosion and maintaining the land's integrity. |
| Atmospheric Regulation | Through the remarkable process of photosynthesis, plants are the primary producers of the oxygen we breathe, while simultaneously absorbing carbon dioxide. This vital exchange purifies our air, making life possible for all animals on Earth. |
| Water Cycle | Plants play a critical role in the water cycle. They draw water from the soil and release it into the atmosphere as vapour through transpiration. This atmospheric moisture then condenses and returns to the Earth as precipitation, sustaining our water sources. |
| Clothing & Textiles | The fibres from plants have long been spun into fabrics, providing us with the materials necessary for clothing and other essential textiles. |
| Food & Sustenance | Plants are the ultimate source of nourishment, providing both direct food for humans (crops) and sustenance for the animals we rely on for food (pastures and foraging). They are the bedrock of our food chains. |
| Aesthetics & Well-being | Beyond their practical uses, plants transform our surroundings into vibrant, beautiful landscapes, enriching our lives aesthetically and contributing to our overall sense of well-being. |
| Climate Stability | By absorbing carbon from the atmosphere and releasing oxygen, plants are our natural allies in combating climate change, helping to maintain a stable global climate for all living things. |
| Natural Pest Control | On farms, native plants attract beneficial insects and birds that prey on agricultural pests. This natural pest control reduces the need for chemical pesticides, leading to healthier crops and a cleaner environment. |
| Pollination & Yield | Native plant areas and wildlife corridors on farms encourage native pollinators, leading to more effective pollination of crops and pastures, which in turn results in higher yields and greater agricultural success. |
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is not just the process of plants; it is a vital part of life on Earth. As it helps in making the food process for plants, from which plants produce energy in the form of glucose and release oxygen, which is of utmost importance for human beings. Plants play the most crucial role in living organisms. Let's plant more trees, save the environment and the future.
