Key Points
- Wilhelm Röntgen discovered X-rays on November 8, 1895, while experimenting with a Crookes tube.
- The accidental discovery of X-rays occurred when a distant screen glowed despite the tube being covered.
- Röntgen won the first Nobel Prize in Physics (1901) and chose not to patent his discovery.
The discovery of X-rays: For more than a hundred years, the inner workings of the human body were a mystery, and the only way to see them was through invasive procedures. Suddenly, an invisible force was let loose in a quiet German lab, which was a stroke of scientific luck. X-rays did more than give us a new way to diagnose things; they changed how we see ourselves and medicine forever.
While recent archival research suggests that American physicist Arthur Goodspeed captured faint, uncredited X-ray-like images in the 1890s, the full understanding, investigation, and formal announcement of the invisible rays belong to one dedicated man. So, who found X-rays in 1895 and made his name famous? A careful German professor has the answer, and his story is a great example of how an observer can be rewarded for looking into something strange.
Who Discovered X-rays in 1895?
Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, a German physicist, is credited with the groundbreaking discovery of X-rays.

Credit - NobelPrize.org
-
Discoverer: Professor Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen (1845–1923).
-
Nationality: German.
-
Date of Discovery: November 8, 1895.
-
Location: Physical Institute of the University of Würzburg, Bavaria, Germany.
-
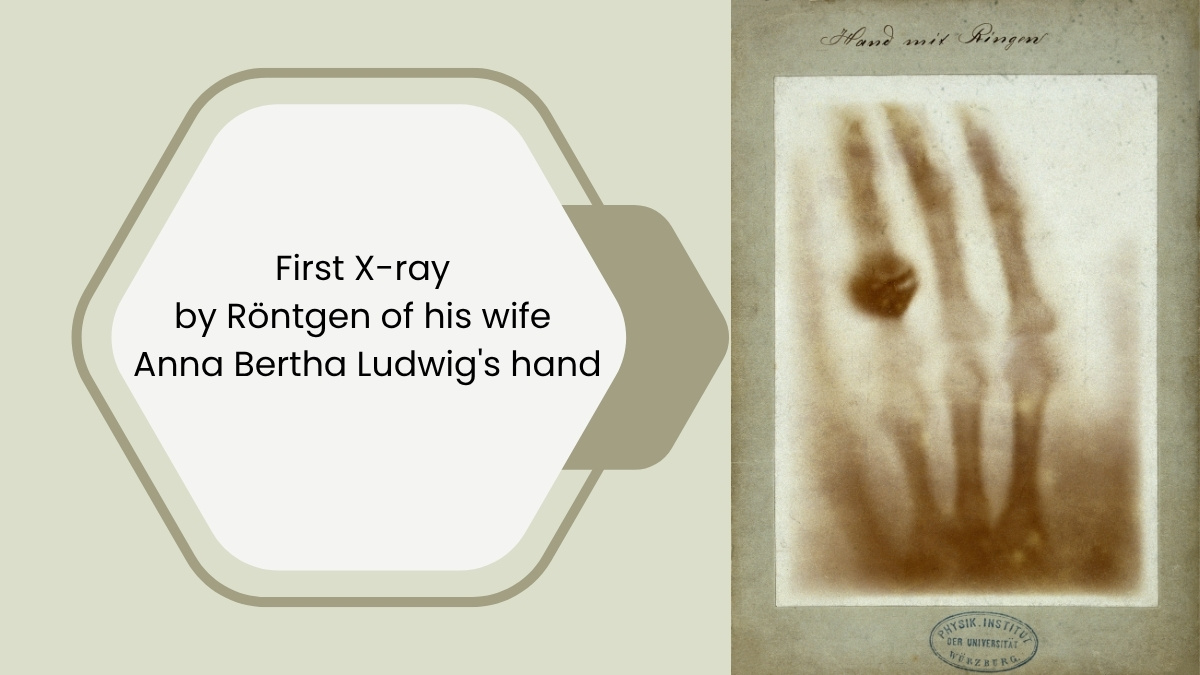
First X-ray Image: On December 22, 1895, he captured the famous X-ray image of his wife’s hand, Anna Bertha, showing her bones and wedding ring.
-
Nobel Prize: In 1901, Röntgen won the first Nobel Prize in Physics for his amazing work. He humbly accepted the prize and didn't try to patent the invention because he thought it should help everyone.
Röntgen called the radiation "X-rays" because "X" is the math symbol for the unknown, since the rays' exact nature was not clear at first.
How Wilhelm Röntgen Accidentaly Discovered X-rays?
The moment the world was given an internal view of the human body came during an experiment focused on something completely different, cathode rays. This is the core of the accidental discovery of X-rays.
Röntgen was studying how electric currents pass through a highly evacuated glass tube known as a Crookes tube (a type of cathode ray tube). To block out all visible light from the tube's operation, Röntgen completely enclosed the Crookes tube in thick, black cardboard.
When he ran a high-voltage electrical current through the covered tube in his dark lab, he saw a faint greenish glow. The glow was coming from a barium platinocyanide-coated screen placed on a bench more than a meter away from the tube.
Since the black paper should have blocked all known light, Röntgen immediately realized that a new, invisible type of ray must be passing from the tube, through the cardboard, and exciting the distant chemical screen. He saw a faint, greenish glow when he ran a high-voltage electrical current through the covered tube in his darkened lab.
Röntgen famously locked himself in his lab for almost six weeks to carefully test and record the properties of this "new kind of ray" before making his results public. This made sure that all of his information was correct.
Credit - Wikipedia
Also Read - All Nobel Prize Winners in Physics (2025 - 1901): Check List
X-rays: The Instant Revolution in Medicine and Science
X-rays had an immediate and widespread effect that went beyond just helping doctors figure out what's wrong.
Medical Diagnostic Leap
Surgeons in Europe and the US started using X-rays just a few weeks after Röntgen made his announcement in early 1896. Early uses included locating bullets, broken bones, and foreign objects inside the body. The practice of radiology was born overnight.
Scientific Advancement
The discovery spurred immense research in physics. Scientists like J.J. Thomson studied the ionization caused by X-rays, which led to the discovery of the electron in 1897. In 1896, while studying X-rays, Henri Becquerel accidentally discovered radioactivity. This was the beginning of nuclear physics.
Modern Applications
X-rays are essential today not only in diagnostic imaging (mammography, CT scans) and radiation therapy (LINAC) but also in areas such as:
-
Airport Security: For scanning luggage.
-
Astronomy: X-ray telescopes study high-energy phenomena in the universe.
-
Industry: Non-destructive testing to find flaws in welded materials and pipelines.
This invisible radiation, which used to be called "X" for unknown, is still a big part of how technology is moving forward today. It is always changing, going from pictures on film to more advanced digital and 3D imaging techniques.
Do You Know - What is Marie Curie Famous for? Know all about Her Life and Legacy
When German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen accidentally became interested in a type of radiation that no one knew about, he changed healthcare forever. It became a very useful tool in medicine. He made the right choice by not patenting the X-ray, which helped it spread quickly around the world. It changed how doctors diagnose patients and opened up new areas of science that still save lives today.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation