Do you remember the Pythagoras Theorem, which you once studied in Mathematics, was a discovery of Pythagoras? In today’s time, people often wonder when Pythagoras was born, his full name, and his contribution to mathematics.
Pythagoras of Samos remains one of history’s most influential figures, is remembered for his profound contributions to mathematics, philosophy, and scientific thought. Although many details of his life come from later ancient sources, his impact is unmistakable. Through this biography, learn about his early life, passion for Mathematics, and his legacy, brought together by the most respected historical references such as Britannica and MacTutor.
Early Life and Background
Pythagoras was born around 570 BCE on the Greek island of Samos. His full name is generally given simply as Pythagoras, as Greek philosophers of the era seldom used surnames. He travelled widely in his youth. According to classical tradition, he visited Egypt, Babylon, and other centres of learning to absorb the knowledge of geometry, astronomy, and religious practices. These journeys shaped much of the life of Pythagoras and his later teachings.
Founder of a Philosophical and Mathematical School
Around 530 BCE, Pythagoras settled in Croton, in southern Italy. There he founded a highly disciplined and mystical community. Members lived communally under strict rules, studied mathematics, music, and ethics, and followed a belief in spiritual purification. This group, known as the Pythagoreans, preserved his ideas and influenced many later thinkers.
Contributions to Mathematics
(Credits: Maths Society)
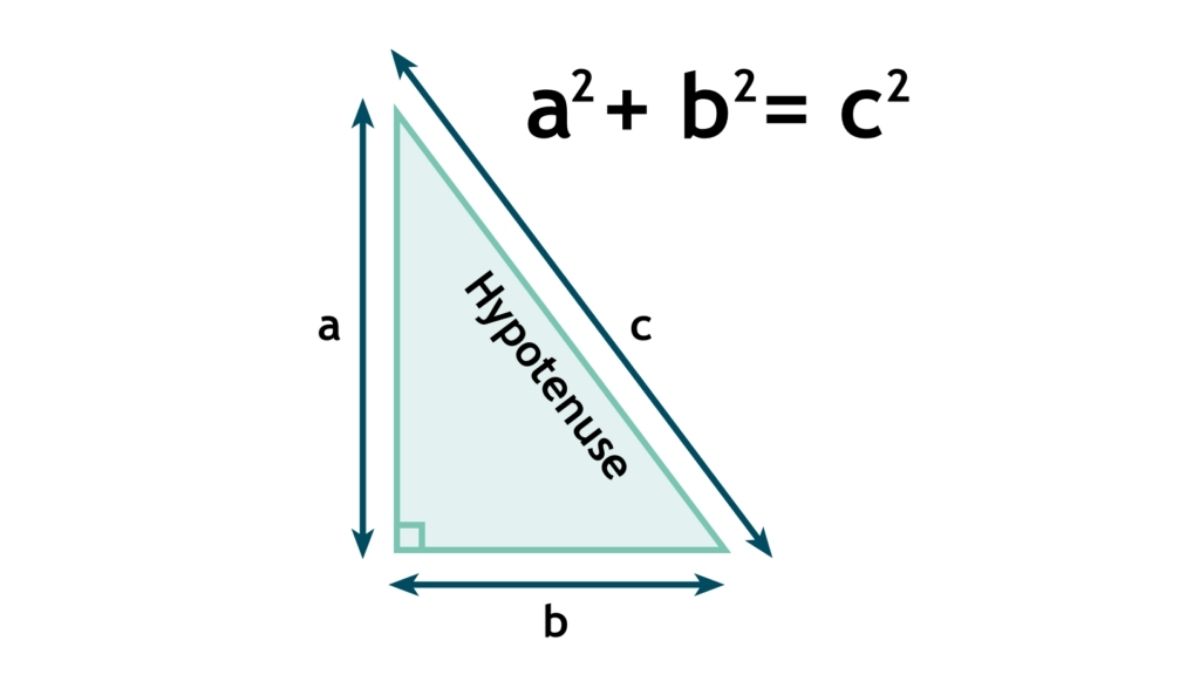
Pythagoras is best known for the "Pythagorean theorem". The formula tells the relationship describing the sides of a right-angled triangle. While the theorem existed in earlier Babylonian mathematics, Pythagoras or his school are credited with its first logical proof. This alone makes him central to the foundations of geometry.
Other notable Pythagoras' contributions to mathematics include:
-
Early work in number theory, classifying numbers as odd, even, triangular, or perfect.
-
The discovery of irrational numbers, particularly the square root of 2.
-
The link between numbers and harmony through Pythagorean tuning shows that musical intervals correspond to whole-number ratios.
-
Influential ideas on cosmology, including the belief that the Earth was spherical.
Because of these contributions, many describe him as the father of mathematics, though the title is also shared with figures such as Euclid and Archimedes.
Also read: List of 9 Greatest Modern Day Mathematicians, Check Here!
Beliefs and Philosophy
Central to Pythagorean philosophy was the idea that “all is number.” The Pythagoreans believed numbers governed the structure of the universe, from geometry to music and moral behaviour. They also taught metempsychosis, the transmigration of the soul, which heavily shaped their ethical rules and way of life.
Legacy
Therefore, Pythagoras is believed to have died around 495 BCE, although the circumstances are unclear. However, his influence has been unprecedented and unquestionable. His ideas shaped Plato, Euclid, and the foundations of Western mathematics, philosophy, and the scientific method.
You may also like to read: What is the Capital of Arizona?
You can also check out our series of articles based on the evolution and disocveries in Mathematics: List of 9 Most Famous Mathematicians in Ancient History, Read Now!
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation