About the IMF
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a global institution committed to fostering sustainable growth and economic stability among its 191 member nations. It achieves this by supporting sound economic policies that encourage monetary cooperation and financial stability—cornerstones for productivity, employment generation, and overall economic prosperity. The IMF is governed by and answerable to its member states.
Where is the IMF headquarters located?
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) headquarters are located in Washington, D.C., United States.
International Monetary Fund (IMF)
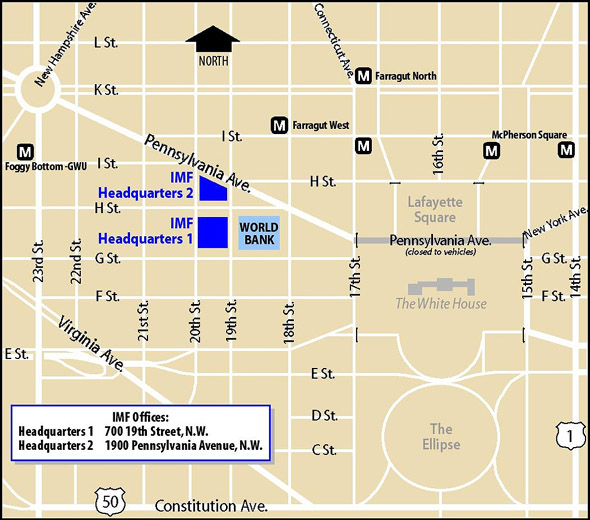
700 19th Street, N.W.
Washington, D.C. 20431
Source: IMF
The IMF headquarters has two buildings: HQ1, whose visitors' entrance is at 720 19th Street, NW, and HQ2, whose visitors' entrance is at the corner of 19th St and Pennsylvania Avenue.
Who is the current managing director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
Source: IMF
Kristalina Georgieva is serving as the current Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). She has been serving as MD of IMF since October 01, 2019, and from October 01, 2024, she began her second term.
What are the objectives of the IMF?
The IMF primarily focuses on three key missions:
-
Promoting international monetary cooperation
-
Facilitating trade expansion and economic development
-
Preventing policies that may hinder global economic growth
To achieve these goals, member countries collaborate with other international organisations under the IMF framework.
Source: IMF
Facts About the IMF in Figures
|
What are the functions of the IMF?
The IMF fosters international financial stability by offering:
1. Policy Advice (Surveillance)
The core responsibility of the IMF is to monitor the economic policies of the 191 member countries of the IMF by providing them policy advice as an activity of surveillance. This surveillance is extended to a global level in each region for helping the developing and underdeveloped countries by identifying their risk areas and ensuring they maintain their economic stability and growth.
2. Lending Support
The IMF behaves as financial assistance to countries facing crises or under weak economic conditions; in this scenario, it is the IMF’s responsibility to give them fiscal breathing space to implement recovery strategies and also make them boost economic growth. It also extends precautionary credit to avoid the potential economic shocks and make them stable.
3. Capacity Development
The IMF helps strengthen national institutions such as central banks, finance ministries, tax authorities, and statistical bodies to enhance economic values at the global level. This includes technical support and training in areas like tax policy, legal frameworks, data management, monetary policy, and governance.
What is the organisational structure of the IMF?
The IMF is governed by its Board of Governors, comprising a governor and alternate from each member country. Its daily operations are managed by a 25-member Executive Board, led by the Managing Director and four deputies. The IMF's 18 departments handle its country, policy, analytical, and technical work. Below in the table, all its details are given:
| Component | Description |
| Board of Governors | Comprises one governor and one alternate governor from each member nation (usually finance ministers or central bank heads). This board holds supreme authority within the IMF. |
| Executive Board | Consists of 25 members responsible for day-to-day operations. |
| Managing Director | Heads the IMF staff and chairs the Executive Board, supported by four Deputy Managing Directors. |
| 18 Departments | Manage country-specific, policy-based, technical, and analytical work. |
How does the IMF make its decisions?
Unlike the United Nations General Assembly, where each country gets one vote, the IMF follows a weighted voting system. A member’s influence is based on its economic standing. The IMF regularly revises this structure to reflect shifts in global economic power, especially recognising the growing role of developing and emerging economies.
Source: IMF
What are the funding sources of the IMF?
The main funding sources of the IMF are Member Quotas, New Arrangements to Borrow (NAB), and Other Bilateral Borrowing Agreements (BBSs). Check all its details given below:
1. Member Quotas
Member contributions—based on their economic size—form the core of IMF resources. These quotas determine voting power and access to IMF financing.
2. New Arrangements to Borrow (NAB)
The NAB acts as a secondary funding source. In 2020, the IMF doubled NAB resources to about SDR 365 billion (approx. $504 billion).
3. Bilateral Borrowing Agreements (BBAs)
Additional funding is provided through agreements with member countries. A 2020 round of BBAs brought in SDR 138 billion (around $190 billion).
What are the key issues on which the IMF focuses?
There are various key issues regarding what the IMF focuses on, given below in detail:
1. Trade
The IMF promotes fair, transparent, and stable trade systems, viewing them as essential for growth and tackling global issues such as climate change, poverty, and food insecurity.
2. Fiscal Policy
The IMF tracks fiscal trends globally and advises countries on spending and taxation strategies to stabilise and boost their economies.
3. Sovereign Debt
Managing national debt has become increasingly challenging, especially for low-income and emerging economies. The IMF works to assess vulnerabilities and propose debt sustainability solutions.
Conclusion
The IMF remains a central pillar of the global economic system. With its focus on monetary cooperation, financial stability, and sustainable growth, the organisation plays a crucial role in supporting countries through economic transitions, crises, and reforms.
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation