CBSE Class 12 Important Chemical Reactions: The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam for 2026 is scheduled for February-March. The exam will cover physical, inorganic, and organic chemistry, so it’s important for students to revise all these sections thoroughly. Being familiar with key reactions in chemistry will save time during the exam and help you answer questions more efficiently.
This article provides a quick revision guide with all the important organic chemistry reactions for Class 12. Students can easily go through these reactions to revise them quickly and effectively. Along with the reactions we are also providing the previous year questions on name reations so that it will be helpful for students. Don’t wait—start your revision now to ensure you're fully prepared!
Important Reactions for Class 12 Chemistry
- Gattermann Reaction:
The Gattermann reaction transforms aromatic compounds into aldehydes using hydrogen cyanide, hydrogen chloride, and a catalyst (aluminium chloride or zinc chloride).
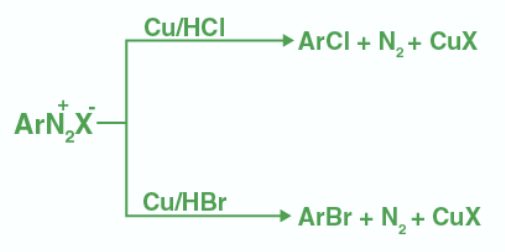
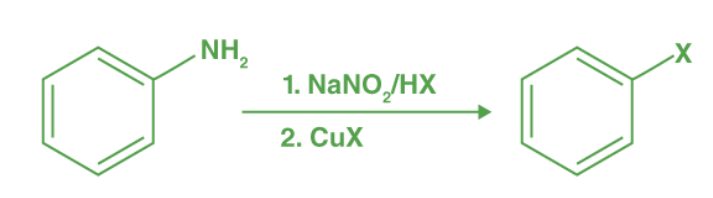
- Sandmeyer Reaction:
Aromatic diazonium salts react with CuCl or CuBr to yield haloarenes (chlorobenzene or bromobenzene). It's a key step in synthesising various aryl halides from aryl diazonium salts.
- Balz-Schiemann Reaction:
The method of preparing arene-diazonium chloride with fluoroboric acid. In this reaction, the arene diazonium fluoroborate is precipitated and decomposes to yield aryl fluoride on heating.
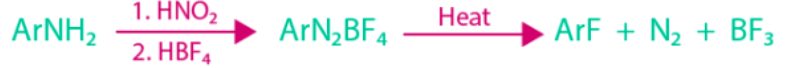
- Swarts Reaction:
When alkyl chloride is heated with a metallic fluoride like AgF, Hg2F2, or SbF3, alkyl fluorides are formed.
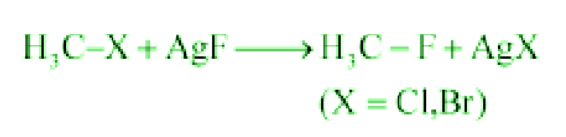
- Finkelstein Reaction:
Alkyl iodides are prepared easily by reacting alkyl chlorides with Nal in dry acetone.
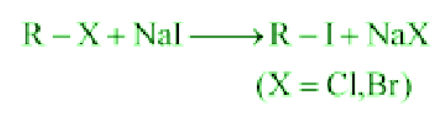
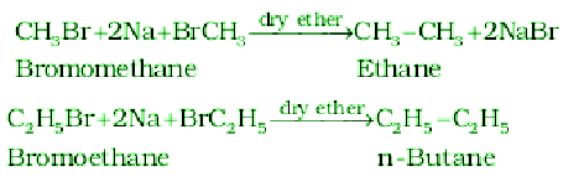
- Wurtz Reaction:
The reaction of Alkyl halides reacts with sodium with dry ether to get hydrocarbons that include the double number of carbon atoms present in the alkyl halide.
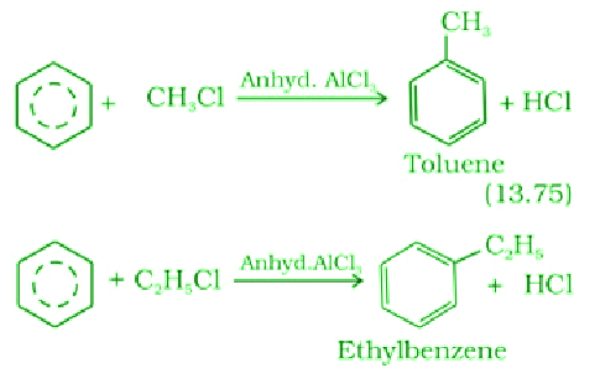
- Friedel-Crafts alkylation Reaction:
Reaction of benzene with an alkyl halide in the presence of anhydrous aluminium chloride to give Alkylbenzene.
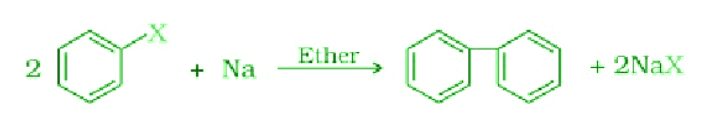
- Fitting Reaction:
The reaction of aryl halides in the presence of sodium in dry ether gives analogous compounds where two aryl groups joined.
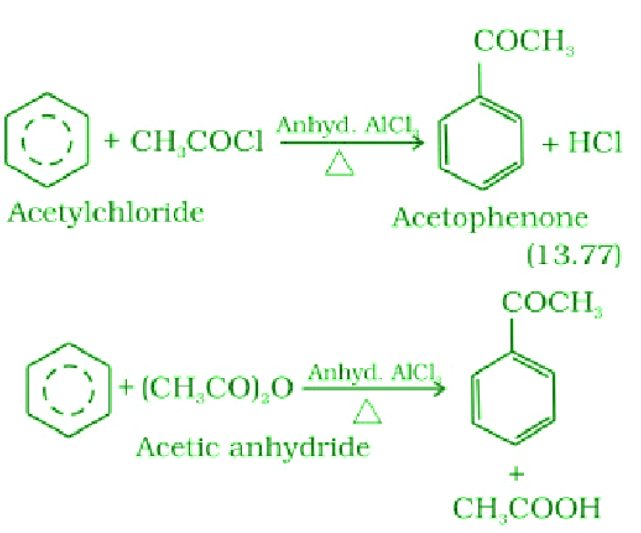
- Friedel-Crafts acylation reaction:
Friedel-Crafts acylation is a chemical reaction that involves the introduction of an acyl group onto an aromatic ring using a Lewis acid catalyst.
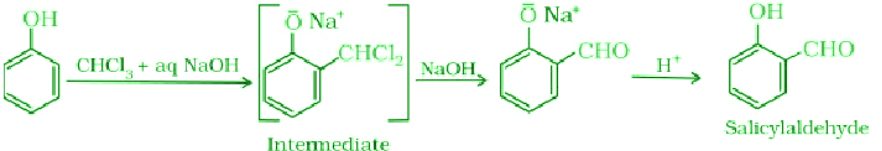
- Reimer-Tiemann Reaction:
Reaction of phenol with chloroform in the presence of sodium hydroxide to introduce -CHO group at the ortho position of the benzene ring. It results in the formation of salicylaldehyde.
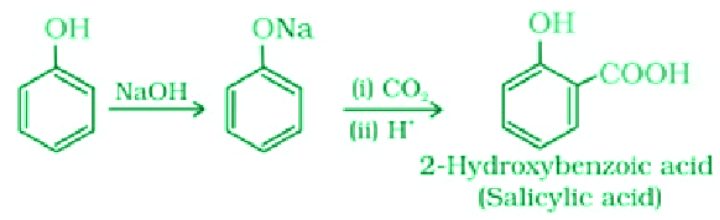
- Kolbe’s Reaction
The reaction of phenol with sodium hydroxide gives sodium phenoxide which further reacts with carbon dioxide in an acidic medium to give 2-hydroxybenzoic acid (Salicylic acid).
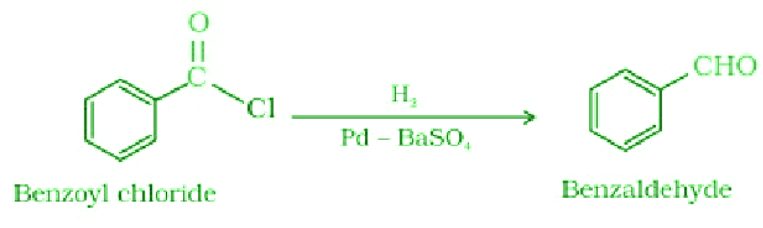
- Rosenmund Reduction:
In this reaction, the acid chlorides are converted into aldehydes in the presence of hydrogen gas over palladium poisoned by barium sulfate.
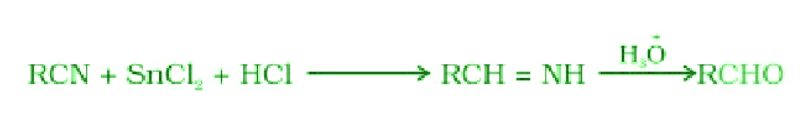
- Stephen reaction:
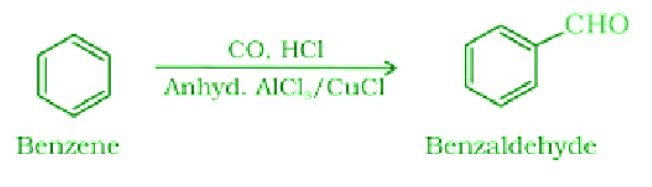
- Gatterman – Koch reaction:
- Clemmensen Reduction:

- Wolff Kishner Reduction:

- Tollens’ test

- Fehling’s test:

- Aldol condensation:
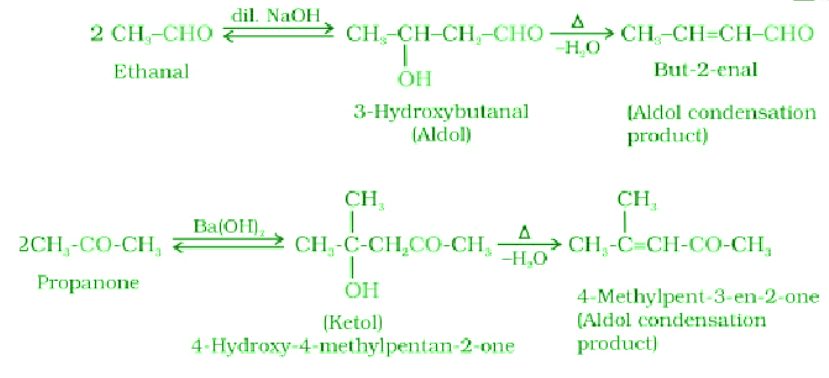
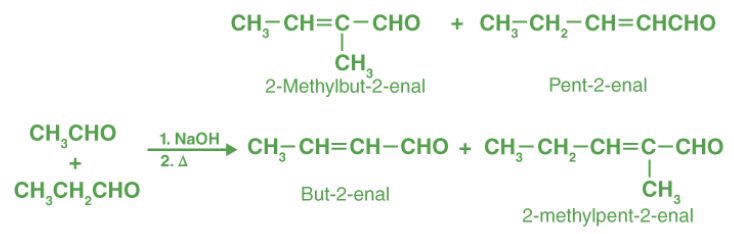
- Cross aldol condensation:
- Cannizzaro reaction:
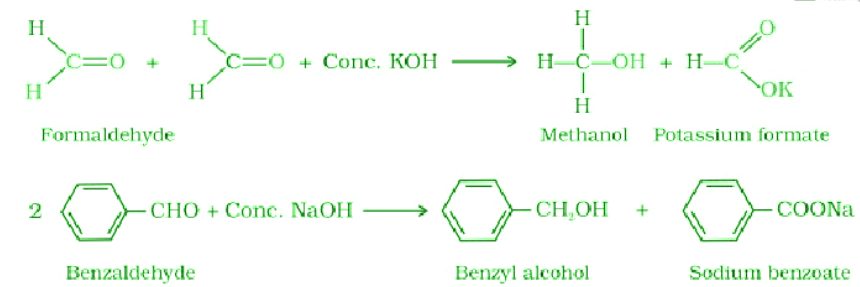
- Kolbe electrolysis:
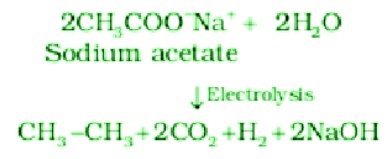
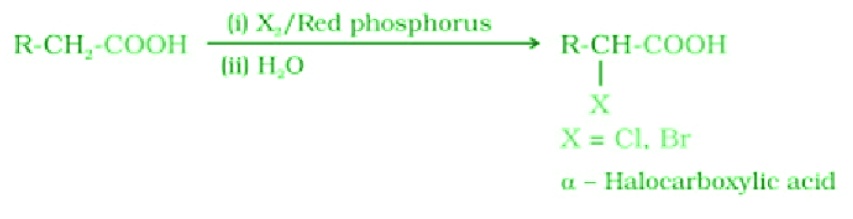
- Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky (HVZ ) reaction:
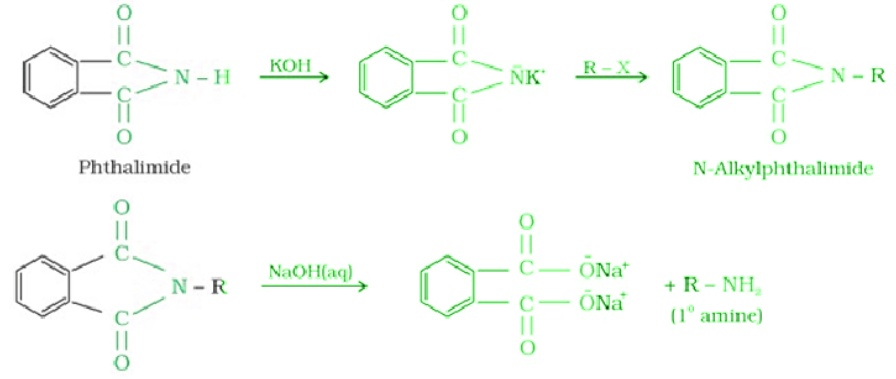
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis:
- Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction:
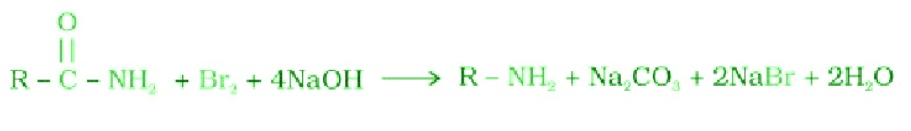
- Carbylamine reaction:
![]()
- Coupling Reactions:
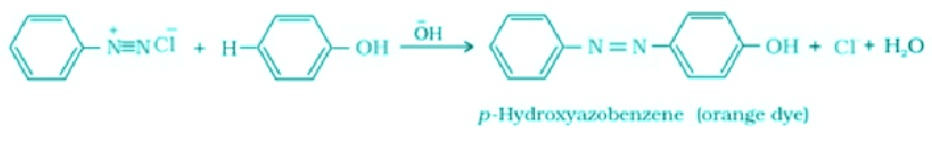
Important Reactions for Class 12 Chemistry from Previous Year
1.
2. Write chemical equations for the following reactions: (Any three)
(a) Hydroboration - oxidation reaction
(b) Williamson Synthesis
(c) Friedel-Crafts Alkylation of Anisole
(d) Reimer-Tiemann Reaction
3. (i) Write equation for preparation of 1-iodobutane from 1-chlorobutane.
(ii) Out of 2-bromopentane, 2-bromo-2-methylbutane and 1-bromopentane, which compound is most reactive towards elimination reaction? 1
(iii) Give IUPAC name of-
4. Write the reagents used in the following reactions:
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
5. Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagents:
(i) HCN (ii) Br2 water
6. What happens when
(i) Phenol reacts with bromine water?
(ii) Anisole reacts with HI?
Write the chemical equations involved in the above reactions.
7. (a) Identify the chiral molecule in the following pair: (i) 3-methylbutan-2-ol (ii) 2,4-dimethylbutan-3-ol
(b) Write the structure of the product when Chlorobenzene is treated with methyl chloride in the presence of sodium metal and dry ether.
(c) Write the structure of the alkene formed by dehydrohalogenation of 1-bromo-1- methylcyclohexane with alcoholic KOH
8.
9.
10.
11. Write mechanism of hydration of ethene to yield ethoxyethane.
12.
13.
(i)Name the reagent used in step 3. What is the necessary condition for this reaction to take place? Name the mechanism.
(ii) At room temperature, the amino acid X exists as a solid. Draw the structure of the solid amino acid.
(iii) With reference to your answer to part (ii), explain why the melting point of the amino acid X is higher than the melting point of CH3CH2CH(OH)COOH
14. Peptides can be hydrolysed into individual amino acids, for example:
(i) How many water molecules would be required to hydrolyse a peptide made from 'n' amino acid molecules?
(ii) Write down the hydrolysis equation for Ala-Ser-Gly.
15. A zwitter ion is a dipolar ion in aqueous solution
Related:
- Top 30+ CBSE Class 12 Chemistry MCQs for Board Exam 2024 with Answers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Deleted syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry sample papers 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24 PDF (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Deleted Syllabus (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Papers with Solution PDF Download
- CBSE Class 12 Additional Practice Questions
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper 2023-24 with Solution and Additional Practice Questions
Also Read:
Comments
All Comments (0)
Join the conversation